Excel: VBA Tips and Tricks
- Published on
- • 4 min read
- Authors
- Name
- Kien
My post here is to keep a reference of the functions and VBA codes I’ve found and modified for my own personal and professional use. I figure I might need these one day.
I deal with Excel spreadsheets at work. One of my favourite things to do is try to automate the work I find by programming in VBA. Below are a few Excel tips and tricks I learned.
Tip #1: Automatically save a spreadsheet using cell reference
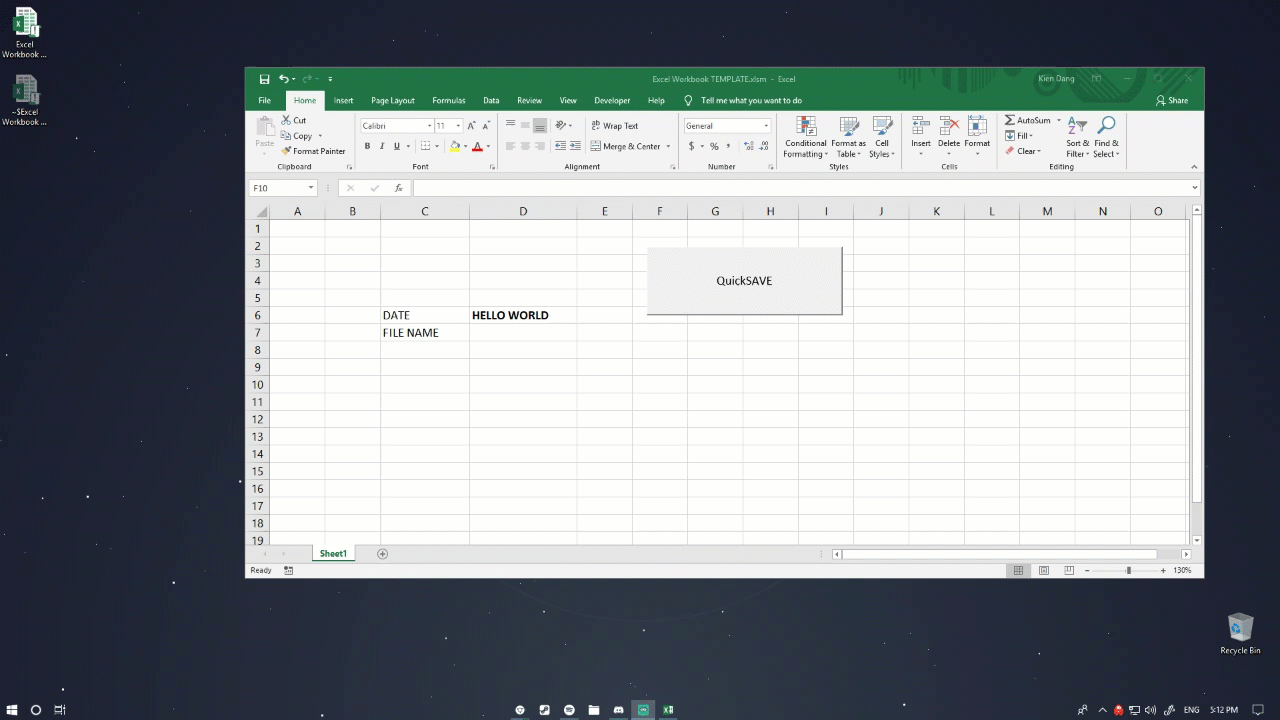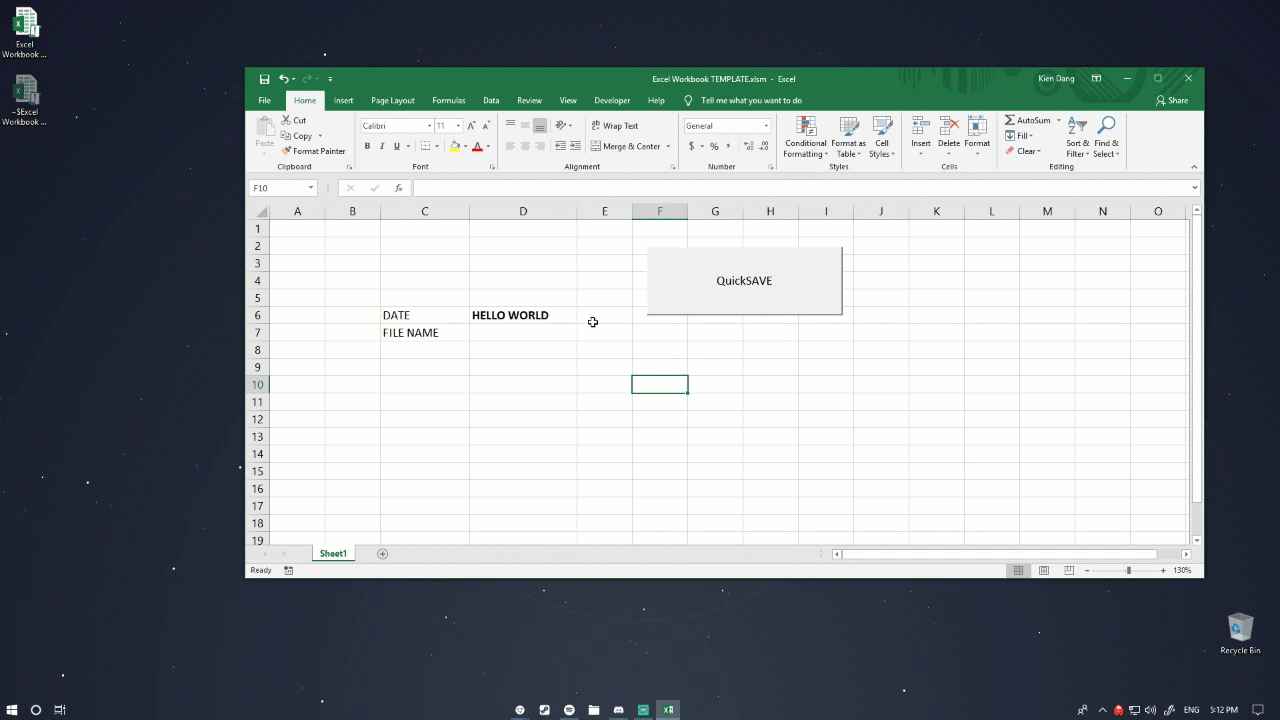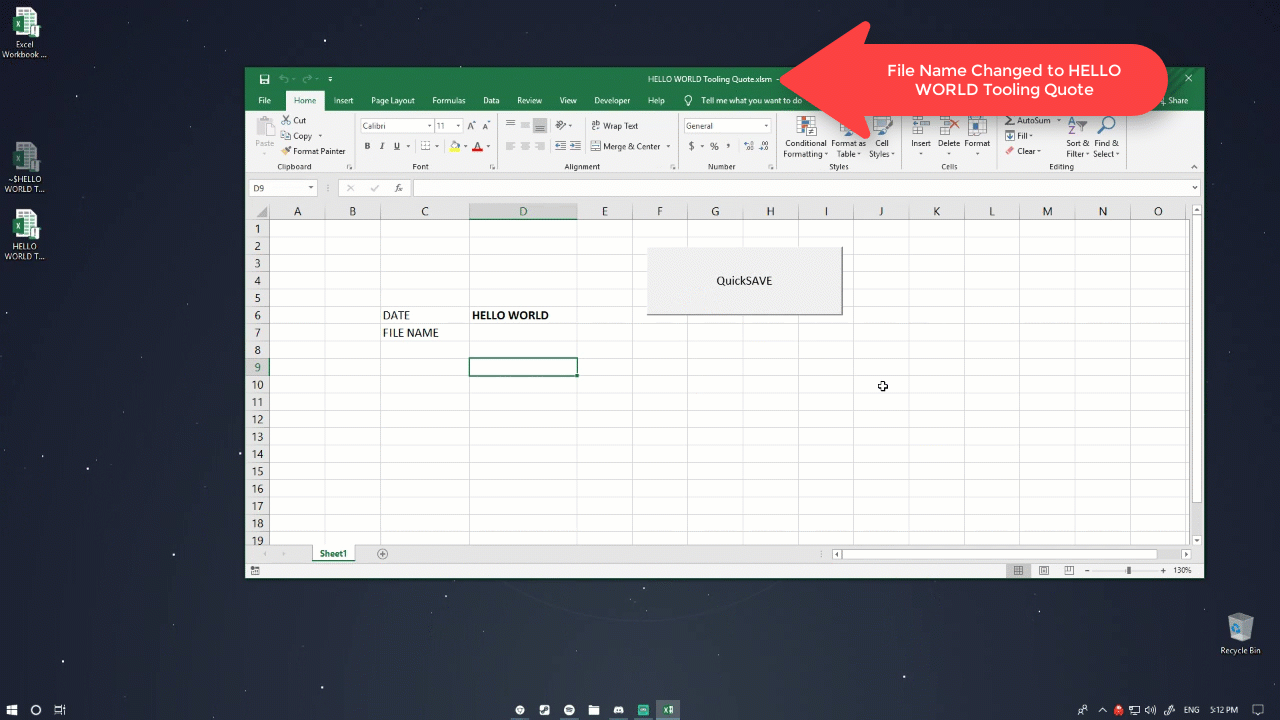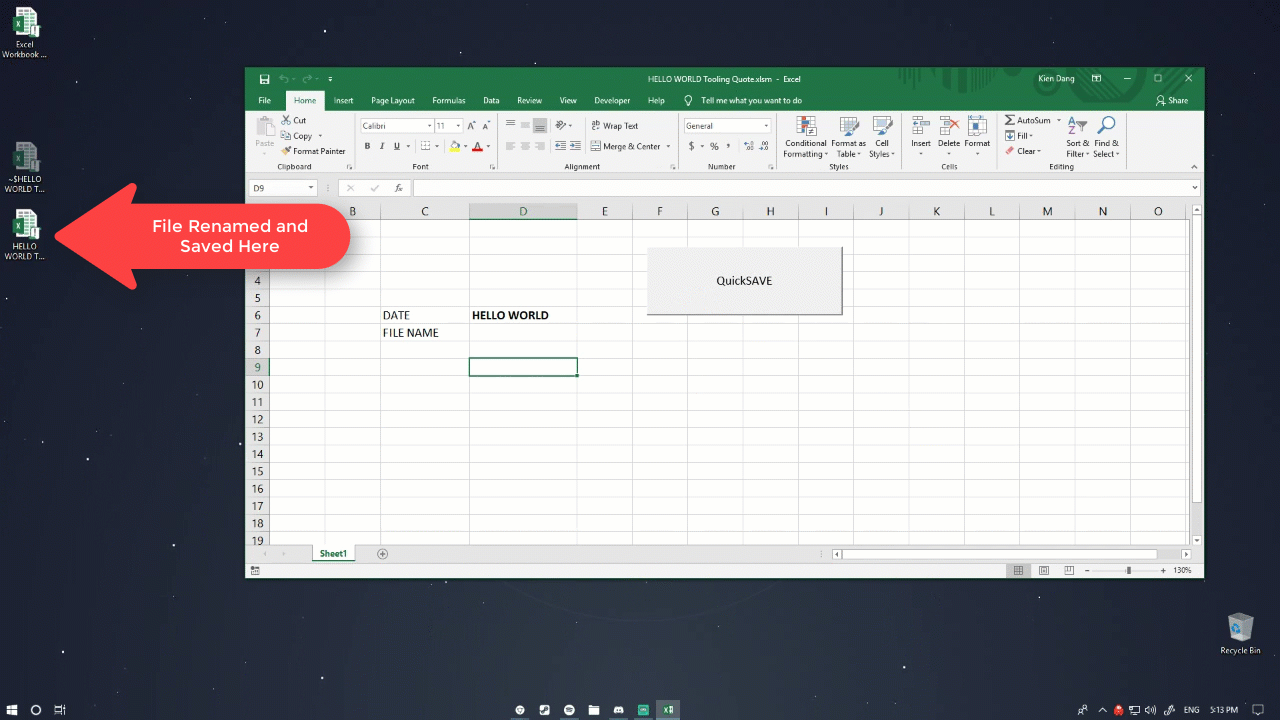
Purpose
It saves the Excel spreadsheet with a referenced cell in your workbook. It will make your workflow faster and prevents the Excel file from being overwritten. The file will save on the path it is currently on. However, you can also tell Excel to save to a certain directory or create new folders using MkDir. Code snippet:
Sub QuickSave() ThisFile = Range("D6").Value & " Tooling Quote" ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:=ActiveWorkbook.Path & "" & ThisFile End Sub
Tip #2: Automatically send emails using Excel**
Purpose
When completing an excel spreadsheet, such as filling out a sales inquiry, the user would want to send the email to the appropriate party to call an action item. The text in the outlook email can be seen in the code snippet, the demo above shows the Excel calling the outlook app and all fields are auto-filled in from the VBA code.
There’s a bit of prep work for this with a combo box and drop downs to bring a cell to someone’s name. Follow this set up by Microsoft here.
The Input Range is the list of names and the Cell Link should point to an empty cell. The Cell Link will call the index starting from 1 in the drop down list and toggle through. An IF statement is then used to reference the Cell Link and generate the email you want the person to be called. Note that the pop up prompt is not necessary, I just added it in there to serve as a reminder to make sure all boxes are filled when completing my work. The VBA code is referenced below:
Sub ReadyToPreferEmail() 'This will automatically set up your outlook
'Updated by Extendoffice 2017/9/14
Dim xOutApp As Object
Dim xOutMail As Object
Dim xMailBody As String
On Error Resume Next
Set xOutApp = CreateObject("Outlook.Application")
Set xOutMail = xOutApp.CreateItem(0)
xMailBody = "Hi, this email was sent by Excel!!! "
On Error Resume Next
With xOutMail
.To = Range("Z12")
.CC = ""
.BCC = ""
.Subject = "Email Sent by Excel VBA - How cool is this"
.Body = xMailBody
.Display
End With
On Error GoTo 0
Set xOutMail = Nothing
Set xOutApp = Nothing
End Sub
Sub YesNoMessage()
Dim Answer As String
Dim MyNote As String
'Place your text here
MyNote = "Do you want to send this email?"
'Display MessageBox
Answer = MsgBox(MyNote, vbQuestion + vbYesNo, "")
If Answer = vbNo Then
MsgBox "Cancelling request"
Else
Call ReadyToPreferEmail
End If
End Sub
In Excel, there is an extremely powerful tool called Macro Recorder. The macro recorder allows the user to perform an Excel task and it will generate the code for that action. For beginners, this is a great way to learn all the functionalities of Excel in the raw VBA language. I used this as a way to find functions that I wanted to automate in excel and put it in a button or assign it in a shortcut. However, when you want to do something very specific, this is where Googling will help and knowing how to find the specific answer to your solution is a satisfying feeling.